Eight Dimensions for Analysis

| Hari Srinivas | |
| Viewpoint Series C-063. |
Abstract
The concept of human security is of paramount importance in today's complex and interconnected world. It underscores the need to prioritize the well-being and protection of individuals and communities, transcending traditional notions of security solely focused on state defense.
By adopting a holistic approach that addresses various dimensions of human vulnerability, such as poverty, conflict, disease, and environmental degradation, human security promotes prevention, empowerment, and resilience.
Upholding human rights, fostering inclusive governance, and promoting sustainable development are central to this paradigm. Governments, businesses, and civil society entities each have distinct roles in advancing human security and must collaborate to address global challenges effectively.
Keywords: human security, well-being, vulnerability, holistic approach, collaboration.
The concept of human security is crucial because it shifts the focus of traditional security paradigms from the protection of states against external threats to the protection and well-being of individuals and communities. Human security emphasizes the intrinsic value of human lives and aims to address the multidimensional challenges that people face in their daily lives.
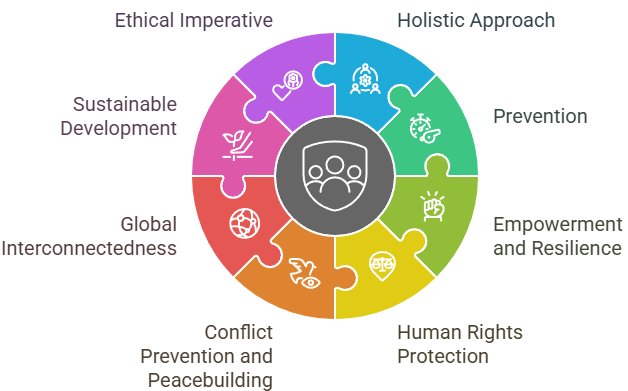
Figure 1: Dimensions of Human Security
Presented below are eight dimensions of the concept of human security that need to be subjected for further analysis - Holistic approach, Prevention, Empowerment and resilience, Human rights protection, Conflict prevention and peacebuilding, Global interconnectedness, Sustainable development, and Ethical imperative.
- Holistic approach:
- Prevention:
- Empowerment and resilience:
- Human rights protection:
- Conflict prevention and peacebuilding:
- Global interconnectedness:
- Sustainable development:
- Ethical imperative:
Human security takes a holistic approach to security concerns, recognizing that threats to individuals' well-being and dignity can come from various sources, including poverty, disease, environmental degradation, violent conflict, and human rights abuses. By considering these interconnected factors, human security seeks to develop comprehensive and integrated strategies to safeguard people's lives and livelihoods.
Rather than solely focusing on responding to crises and conflicts after they have occurred, human security encourages proactive measures to prevent these issues from arising in the first place. By addressing root causes and underlying vulnerabilities, human security initiatives can help reduce the likelihood of conflicts and crises.
Human security aims to empower individuals and communities to be more resilient in the face of challenges. By addressing socioeconomic disparities, providing access to education, healthcare, and social services, and fostering inclusive governance, human security initiatives can strengthen communities and their capacity to cope with adversity.
Central to the concept of human security is the protection of human rights. Ensuring that people can live with dignity and in an environment that respects their fundamental rights is a core principle of human security. This includes safeguarding civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights.
Human security emphasizes addressing the underlying drivers of conflicts and promoting conditions for sustainable peace. By addressing the grievances and insecurities of individuals and communities, human security can contribute to the prevention of conflicts and the building of lasting peace.
In an increasingly interconnected world, the security of one country or region can have significant implications for others. Transnational challenges like pandemics, terrorism, and environmental crises require international cooperation and a human security approach that transcends national borders.
Human security and sustainable development are closely linked. Development efforts that prioritize human security considerations can lead to more equitable, inclusive, and sustainable outcomes, benefiting both present and future generations.
Viewing security through a human-centric lens reflects an ethical imperative to prioritize the well-being and dignity of individuals. Human security reflects a commitment to human rights and the value of every human life, regardless of nationality, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status.
|
|
|
|
Return to Human Security Contact: Hari Srinivas - hsrinivas@gdrc.org |
