
| Hari Srinivas | |
| Concept Note Series C-050. |
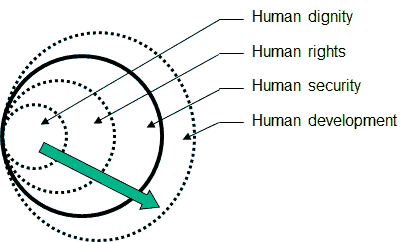
Human dignity, human rights, human security, and human development are interconnected concepts that form a continuum, each building upon and supporting the others. Let's explore how these concepts are connected:
The interconnected concepts related to Huamn Security
The concepts of human dignity, human rights, human security, and human development are intrinsically interconnected, forming a cohesive framework for promoting and safeguarding the well-being of individuals and societies. At the core of this linkage lies the recognition and respect for the inherent worth and value of every human being, which is the essence of human dignity.
Human rights serve as a fundamental aspect of human dignity, encompassing a set of universal entitlements and freedoms that all individuals should enjoy, irrespective of their background or circumstances. These rights include civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights, aiming to protect individuals from discrimination, oppression, and exploitation. By upholding human rights, societies create an environment where people can live with dignity and thrive, fostering a sense of inclusivity, equality, and justice.
Human security extends the concept of human dignity and human rights to address broader threats to individuals and communities. It encompasses protection from not only physical violence and conflict but also other forms of insecurity, such as poverty, disease, environmental hazards, and social marginalization. Human security acknowledges the interconnectedness of various threats and emphasizes the importance of addressing the root causes to ensure the holistic well-being of individuals and societies. When people feel safe and free from pervasive threats, they can fully participate in social, economic, and political activities, contributing to their own and their community's development.
Human development complements the notions of human dignity, human rights, and human security by emphasizing the importance of enabling individuals to lead fulfilling lives and reach their full potential. It encompasses a broader understanding of development beyond mere economic growth, encompassing improvements in education, healthcare, social inclusion, and access to opportunities. When societies prioritize human development, they invest in the capabilities and empowerment of their citizens, leading to greater overall progress and prosperity. By linking human dignity, human rights, human security, and human development, societies can create a virtuous cycle that fosters inclusive and sustainable growth, ultimately promoting the well-being and dignity of all individuals.
- Human Dignity: Human dignity refers to the inherent worth and value of every individual, simply by virtue of being human. It recognizes the fundamental equality and inviolability of all individuals. Human dignity serves as the foundation for the other concepts.
- Human Rights: Human rights are the legal, moral, and ethical entitlements that individuals possess by virtue of their humanity. They are based on the principles of human dignity and provide a framework for the protection and promotion of individuals' well-being. Human rights encompass civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights, ensuring that individuals have the freedom, equality, and opportunities necessary for a dignified life.
- Human Security: Human security focuses on protecting and empowering individuals from various threats that undermine their well-being and dignity. It encompasses both traditional and non-traditional security concerns, such as armed conflict, poverty, disease, environmental degradation, and human rights abuses. Human security emphasizes the holistic and comprehensive approach to safeguarding individuals and communities.
- Human Development: Human development refers to the process of expanding people's freedoms and capabilities, enabling them to lead lives they value and realize their full potential. It encompasses various dimensions, including health, education, income, social inclusion, and political participation. Human development seeks to enhance people's well-being and dignity by addressing the multidimensional aspects of their lives.
The continuum emerges from the interplay between these concepts. Human dignity provides the underlying principle that guides the recognition of human rights. Human rights, in turn, serve as the framework for protecting and promoting individuals' well-being, which contributes to human security. Human security, with its focus on protecting individuals from various threats, creates an environment conducive to human development. Human development, by addressing the multidimensional aspects of people's lives, fosters the realization of human rights and enhances human dignity.
Human dignity sets the foundation for human rights, which provide the framework for protecting and promoting well-being. This, in turn, contributes to human security, creating the conditions necessary for human development to flourish. The continuum signifies the interconnectedness and mutual reinforcement of these concepts, all working towards ensuring individuals' flourishing and the realization of their full potential.
In addition to the above concepts, several other concepts can be added to the continuum, further enriching the understanding of human well-being and flourishing. Here are a few examples:
These additional concepts further expand the continuum by emphasizing the importance of social justice, the rule of law, environmental sustainability, gender equality, and peace in promoting human well-being. Together with human dignity, human rights, human security, and human development, they form a broader framework for understanding and promoting the holistic flourishing of individuals and societies.
|
|
|
|
Return to Human Security Contact: Hari Srinivas - hsrinivas@gdrc.org |
